Features
|
・Soft couplings reduces loss of rotational energy. ・Also effective for mechanisms with low torque on the drive side which require accuracy and atable rotation. ・High reliability design, with roughly 10 times the rotation lifespans of UJ and GJ couplings. ・electrical insulation:1000V |
 |
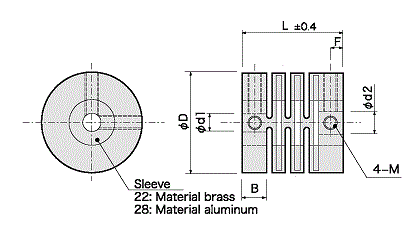
Configuration and materials
|
|
Cautions when using plastic couplings |
Dimensions
| Item No. | D |
Standard hole diameters ød1,ød2 H8 (left/right can be freely conbined) | L | F | B | M | Fastening torque (N⋅m) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGJ/EGP |
22 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 22.2 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 3 | 0.7* | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 32 | 3.6 | 8.8 | 4 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
*φ8 fastening torque = 0.3N・m
Specifications
|
Item No. |
Allowable torque (N⋅m) |
Maximum Rotating speed (rpm) | Torsional rigidity (N⋅m/rad) |
Allowable parallel misalignment (mm) |
Allowable angular misalignment (°) |
Allowable end play (mm) | Moment of inertia (kg⋅m2) | Mass | Materials | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | ||||||||||
| EGJ | 22 | 1.0 | 8,000 | 20 | 0.6 | 6 | ±0.6 | 4x10-7 | 13 | POM |
| EGP | 22 | 1.6 | 12,000 | 40 | 0.4 | 4 | ±0.4 | 4x10-7 | 13 | Glass-fiberreinforced resin |
| EGJ | 28 | 1.8 | 8,000 | 40 | 0.6 | 5 | ±0.8 | 3.4x10-6 | 26 | POM |
| EGP | 28 | 3.0 | 12,000 | 100 | 0.4 | 4 | ±0.5 | 3.4x10-6 | 26 | Glass-fiberreinforced resin |
・Heat resistance (ambient temperature):GF resin,-30℃ to 85℃
・Note:When the ambient temperature to be used is the maximum, the permissible torque is 1/2 of the value in the table.